Quick Navigation:
- What Data Wiping Involves
- Difference Between Data Wiping and Simple Deletion
- Common Scenarios for Using Data Wipers
- How Data Wipers Work?
- How to Choose the Right Data Wiper?
- Best Practices for Data Wiping
- Conclusion
In this modern world, securing data has become increasingly critical. One essential tool in ensuring that sensitive information is effectively removed is a data wiper. This article explores what a data wiper is, how it works, the different types available, best practices for use, and the challenges associated with data wiping.

What Data Wiping Involves
Data wiping, often referred to as data erasure, is the process of securely removing data from a storage device to ensure that it cannot be recovered or reconstructed. Unlike simple file deletion or formatting, which only removes file pointers and makes the data invisible to the operating system, data wiping involves overwriting the data multiple times. This ensures that the original data is rendered completely unrecoverable.
Difference Between Data Wiping and Simple Deletion
Simple deletion or formatting of a disk does not actually remove the data from the storage medium; it merely removes the pointers to the data. This means that the data can often be recovered using specialized software. Data wiping, on the other hand, goes beyond this by physically altering the data on the disk through overwriting or other methods, making it impossible to retrieve.
Common Scenarios for Using Data Wipers
1. Device Disposal
When retiring or decommissioning old devices, such as computers, hard drives, or smartphones, it is crucial to ensure that no personal or sensitive data remains accessible. Data wipers are used to securely erase all information from the storage medium, preventing any potential recovery by unauthorized individuals. This is especially important for businesses and individuals who want to protect their privacy and prevent identity theft or data breaches.
2. Data Breaches
During data breach where a device or storage medium has been compromised, data wiping becomes essential to prevent further unauthorized access to sensitive information. By using data wipers, organizations can ensure that any potentially exposed data is thoroughly erased from the device before it is repaired, disposed of, or repurposed. This helps mitigate the risk of data leakage and protects against further exploitation of compromised information.
3. Compliance
Many organizations are required to compliance to data protection regulations and standards, such as GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS. These regulations often mandate that data must be securely erased before equipment is discarded, sold, or repurposed. Data wipers are used to meet these compliance requirements by ensuring that all data on storage media is irretrievably removed. This helps organizations avoid legal penalties and maintain data security standards.
How Data Wipers Work?
Overview of the Wiping Process:
Data wipers are designed to securely erase information from storage devices to prevent unauthorized recovery. The core process involves replacing existing data with new data patterns or disrupting the physical media to render the original data irretrievable. The process generally includes several steps:
- Selection: The user selects the drive or files to be wiped. Depending on the tool, this can involve choosing specific files, entire partitions, or the whole drive.
- Method Selection: The user chooses a wiping method or standard. Different methods offer varying levels of security and effectiveness.
- Execution: The data wiper performs the selected method, overwriting data or disrupting the storage media.
- Verification: Many tools provide a verification step to confirm that the data has been effectively erased. This can include generating reports or performing a scan to ensure that no recoverable data remains.
Methods Used for Data Wiping:
1. Overwriting
Overwriting is the most common method used by data wipers. On a storage device, it entails writing fresh data over the old data. This method can be performed using various patterns and numbers of passes:
- Single Pass: Writes new data over the old data once. This method is fast but less secure.
- Multiple Passes: Involves writing new data over the old data multiple times. Standards like DoD 5220.22-M recommend multiple passes (e.g., three) to increase security by making data recovery more difficult.
- Random Data: Writes random patterns or data to ensure that the original data cannot be reconstructed.
2. Degaussing
Degaussing involves using a strong magnetic field to disrupt the magnetic domains on a hard disk drive (HDD). This method effectively erases the data stored on magnetic media. However, it does not work on solid-state drives (SSDs) or other types of non-magnetic storage.
- Electromagnetic Field: Generates a powerful magnetic field to scramble the data.
- Limitations: Effective only for magnetic storage media and not suitable for SSDs or flash drives.
3. Physical Destruction
The most thorough technique of data wiping is physical destruction, which entails physically harming the storage device to eliminate any chance of data retrieval. This can include:
- Shredding: Using mechanical devices to shred the drive into small pieces.
- Crushing: Applying pressure to physically deform the drive and destroy its components.
- Incineration: Burning the storage device to render it completely unusable.
- Effectiveness: This technique guarantees that the data is unrecoverable but is typically used as a last resort due to its irreversible nature and environmental concerns.
Common Data Wiping Standards and Protocols:
1. DoD 5220.22-M
The Department of Defense (DoD) 5220.22-M is a data wiping standard developed by the U.S. Department of Defense. It specifies methods for sanitizing data storage devices:
- Three Passes: The standard requires three passes of overwriting with different patterns to ensure thorough erasure.
- Verification: It includes a verification step to ensure the data has been successfully erased.
- Use: Widely adopted in both governmental and private sectors for its rigorous approach to data destruction.
2. NIST 800-88
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) Special Publication 800-88 provides guidelines for media sanitization. It outlines several methods for data wiping and disposal:
- Clear: Overwriting data to make it inaccessible but not physically destroyed.
- Purge: More rigorous methods, such as multiple overwrites, to ensure data cannot be recovered.
- Destroy: Physical destruction of the media to ensure complete data removal.
- Guidance: Provides detailed procedures and best practices for sanitizing various types of storage media, including HDDs, SSDs, and flash drives.
How to Choose the Right Data Wiper?
To choose the right data wiper, follow these steps:
- Identify Your Storage Media: Ensure the wiper works with the type of storage you're using (HDD, SSD, USB drive, etc.).
- Determine Security Needs: Choose a wiper based on how sensitive your data is. For high-security needs, look for tools that follow strict standards and offer multiple overwriting passes.
- Check Usability: Opt for tools that are easy to use and have features like automation if needed.
- Consider Cost: Free tools are fine for basic needs, but paid options might offer more features and better support.
- Look for Support and Updates: Make sure the tool has good support and is regularly updated.
DoYourData Super Eraser is one of the best data wipers. It can help you securely and permanently erase data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, SD card, USB drive, digital camera, etc.
DoYourData Super Eraser
- Three flexible data erasure modes: erase files, wipe hard drive, wipe free disk space.
- Securely and permanently erase data from HDD, SSD, external storage device.
- The erased data is gone forever, can't be recovered by any data recovery method.
Follow the steps below to wipe a hard drive by using DoYourData Super Eraser:
Step 1. Download and install DoYourData Super Eraser on your computer and make sure the target hard drive is connected to your computer.
Step 2. Choose Wipe Hard Drive mode, then select the target hard drive, click on Wipe Now button.
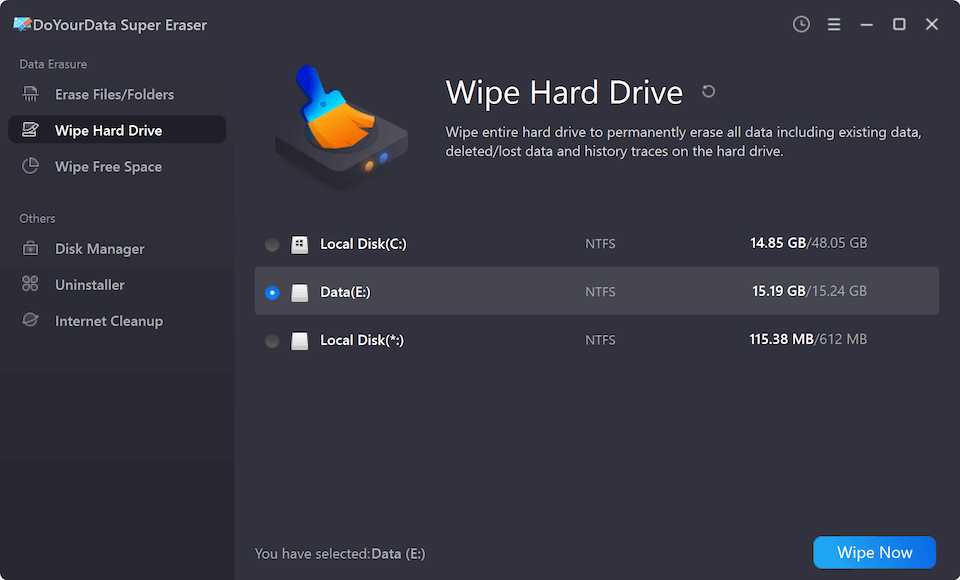
Step 3. Select a data erasure standard, then click on Continue button.
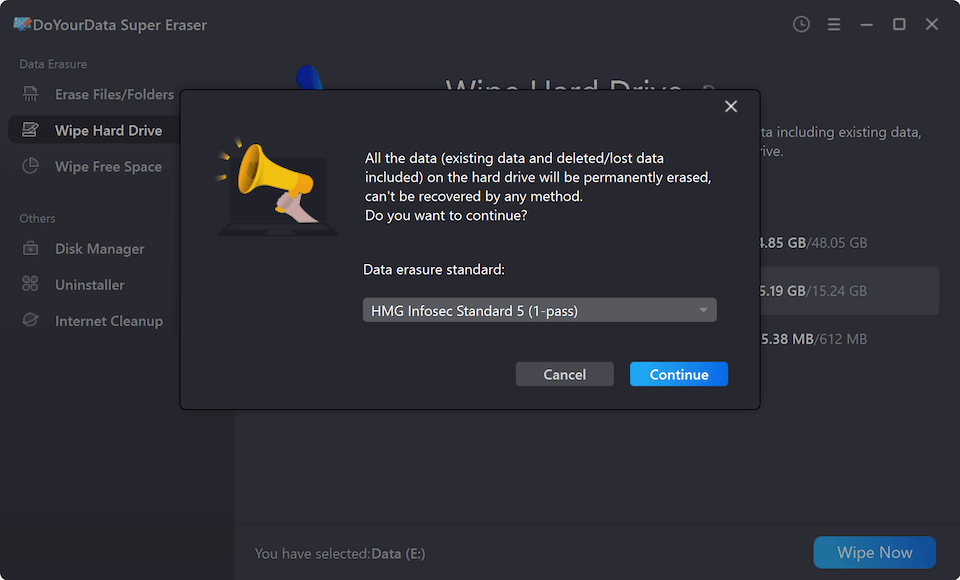
Step 4. Securely format and wipe the selected hard drive.
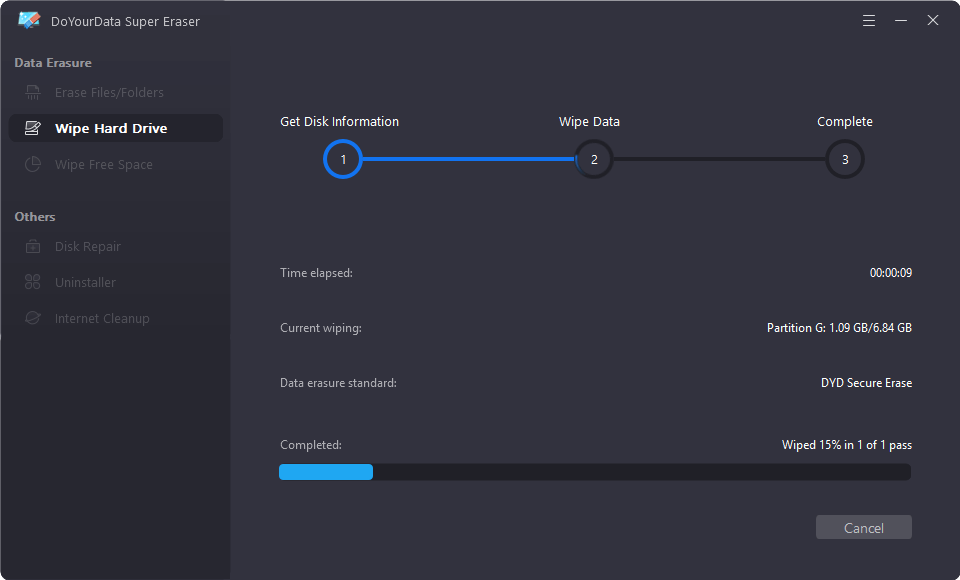
Step 5. Once the data is erased, it is lost for good, cannot be recovered by any method.
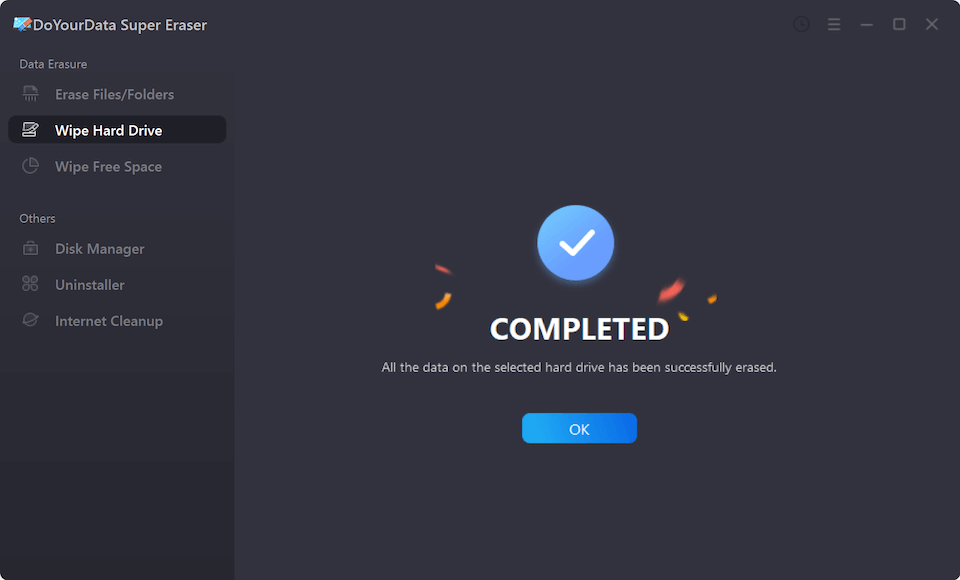
Note: DoYourData Super Eraser is a 100% safe and effective data wiper. Once the data is erased by DoYourData Super Eraser, the data is lost for good, cannot be recovered by any method. So, please make a backup before wiping your drive with DoYourData Super Eraser.
Best Practices for Data Wiping
Ensuring Complete Data Removal:
To ensure data is completely removed, use data wiping tools that follow established standards and perform multiple passes. Verify that the process is complete by using verification features or secondary tools.
Verifying the Effectiveness of the Wiping Process
Many data wiping tools provide reports or certificates of erasure. Keep these records for compliance and future reference.
Compliance with Data Protection Regulations and Standards
Adhere to data protection regulations by choosing tools that comply with standards like DoD 5220.22-M or NIST 800-88. Ensure that all data wiping processes are documented and verifiable.
Limitations and Challenges:
Potential Issues with Data Wiping
- Incomplete Wiping
- Issue: If the data wiping process is interrupted or if the tool malfunctions, some data may not be fully erased and could remain recoverable.
- Impact: This can lead to partial data recovery, compromising data security.
- Solution: Ensure that the wiping process is completed without interruptions and verify the results using built-in verification features or additional tools.
- Hardware Failures
- Issue: Malfunctions or errors in hardware-based data wiping methods, such as degaussers or shredders, can impact their effectiveness.
- Impact: Faulty hardware can result in incomplete data destruction, leaving data potentially recoverable.
- Solution: Regularly maintain and calibrate hardware tools, and use reputable devices with proven reliability.
Specific Challenges with Newer Technologies
- Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
- Issue: SSDs use flash memory and advanced technologies like wear leveling, which can make traditional data wiping methods less effective. Overwriting data may not fully erase information due to the way data is managed on SSDs.
- Impact: Standard wiping techniques may not completely remove data from SSDs, posing a risk for data recovery.
- Solution: Use specialized SSD erasure methods or tools provided by the SSD manufacturer that are designed to handle flash memory technology. For secure data deletion, leveraging the built-in "Secure Erase" feature of SSDs is often recommended.
Mitigating Risks Associated with Data Wiping
- Regular Testing
- Practice: Regularly test and verify the effectiveness of your data wiping methods to ensure they are working as intended.
- Benefit: This helps confirm that data is being securely erased and reduces the risk of data recovery.
- Use Trusted Tools
- Practice: Choose well-regarded and reliable data wiping tools that are recommended by experts and adhere to industry standards.
- Benefit: Trusted tools are more likely to perform data wiping effectively and include features for verification and compliance.
By addressing these limitations and challenges, you can enhance the effectiveness of your data wiping processes and better protect sensitive information from unauthorized recovery.
Conclusion
Data wiping is a critical process for protecting sensitive information and ensuring that data is irretrievably removed from storage devices. Understanding the methods and tools available, along with best practices and challenges, can help you make informed decisions about data security. Whether using software-based tools or hardware solutions, ensuring compliance with standards and verifying the effectiveness of the process are essential steps in safeguarding your data from unauthorized access.
DoYourData Super Eraser is a reliable data wiper tool for both Windows and macOS. It can help you securely and permanently wipe data from HDD, SSD, USB flash drive, SD card or other storage device with certified data standards. No physical damage. If you will sell, donate or dispose of your old HDD/SSD, you can use this data wiper to securely wipe the drive and permanently erase all your private data from it.

DoYourData Super Eraser
DoYourData Super Eraser, the award-winning data erasure software, offers certified data erasure standards including U.S. Army AR380-19, DoD 5220.22-M ECE to help you securely and permanently erase data from PC, Mac, HDD, SSD, USB drive, memory card or other device, make data be lost forever, unrecoverable!